Share this
Every so often, the cosmos offers us a rare spectacle that transcends the ordinary, captivating both scientists and casual observers alike. One such phenomenon is the total solar eclipse—a breathtaking event that plunges day into an eerie twilight and unveils the celestial mechanics at play in our solar system. Whether you’re a seasoned astronomer or simply an enthusiast of the night sky, here’s what you need to know about this awe-inspiring event.
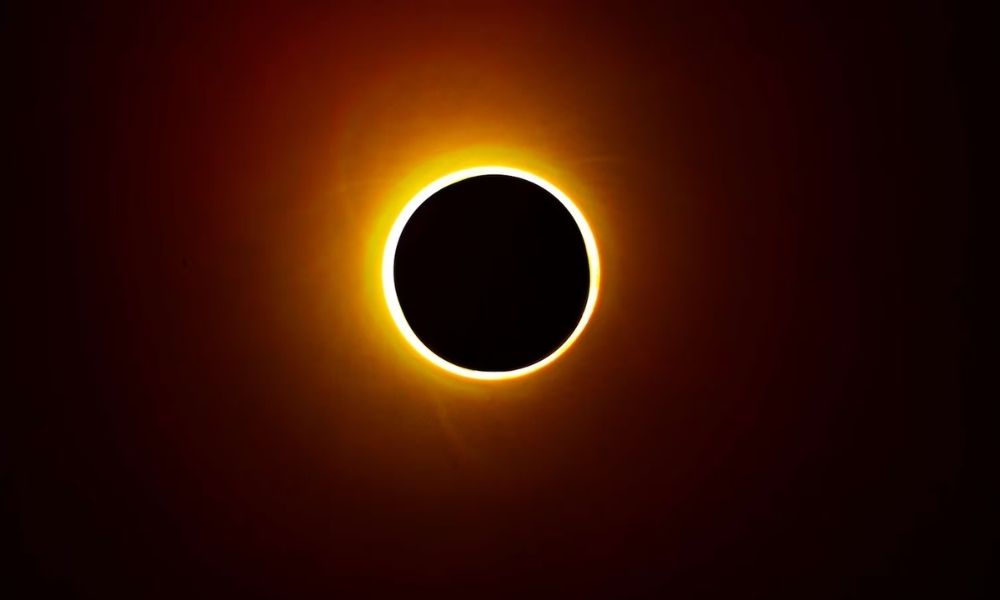

1. What is a Total Solar Eclipse?
A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes directly between the Earth and the Sun, obscuring the Sun’s disk entirely or creating a ring of fire effect known as an annular eclipse. During this alignment, the Moon casts its shadow upon the Earth, blocking the Sun’s light in certain regions and causing a temporary blackout known as totality.
2. Path of Totality
The path of totality refers to the narrow track along which the total eclipse is visible. This path can span thousands of miles but is often only a few dozen miles wide. Observers within this path experience the full glory of the eclipse, while those outside witness a partial eclipse, where only a portion of the Sun is obscured.
3. Totality Duration
The duration of totality varies with each eclipse and depends on factors such as the Earth’s distance from the Sun and the Moon’s distance from the Earth. Typically, totality lasts for just a few minutes, ranging from a few seconds to a maximum of about seven and a half minutes.
4. Safety Precautions
Observing a solar eclipse, whether total or partial, requires caution to protect your eyes. Staring directly at the Sun, even when it’s partially obscured, can cause permanent eye damage or blindness. Specialized solar filters, such as eclipse glasses or solar viewing goggles, are essential for safe viewing. Alternatively, you can use indirect viewing methods, such as a pinhole projector or a solar viewing telescope, to witness the eclipse safely.
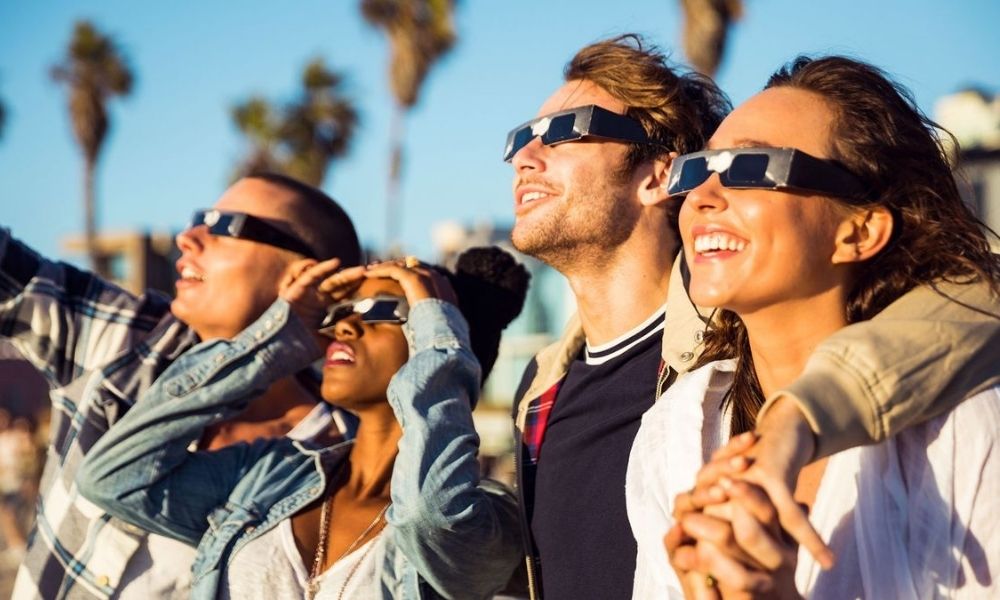

5. Rare and Transient Phenomenon
Total solar eclipses are relatively rare events, occurring somewhere on Earth approximately every 18 months. However, their visibility is limited to specific regions, making each occurrence a fleeting opportunity for those fortunate enough to be in the path of totality. Due to the Earth’s rotation and the Moon’s orbit, no two solar eclipses are exactly alike, adding to their mystique and allure.
6. Cultural and Historical Significance
Throughout history, solar eclipses have inspired awe and wonder across cultures worldwide. Ancient civilizations often interpreted eclipses as omens or celestial battles between mythical deities. Today, eclipses continue to captivate people’s imaginations, serving as opportunities for scientific discovery, cultural celebrations, and communal gatherings.
7. Planning Your Eclipse Experience
For avid eclipse chasers or those simply curious about this cosmic spectacle, planning ahead is crucial. Eclipse enthusiasts often travel great distances to witness totality firsthand, researching weather patterns and logistical considerations to maximize their viewing experience. Websites and apps dedicated to eclipse forecasting and tracking can help you determine the best viewing locations and times for upcoming eclipses.
Conclusion
A total solar eclipse is a profound natural phenomenon that reminds us of our place in the vast expanse of the cosmos. Whether you’re gazing up in wonder from within the path of totality or observing a partial eclipse from afar, the experience of witnessing such a rare event is unforgettable. As you prepare for the next total solar eclipse, remember to prioritize safety, plan your viewing location, and embrace the opportunity to marvel at the wonders of the universe.


0 Comments